Closure in JS
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
The closure is a function that is bound together with its lexical environment.
- Lexical environment is an environment where the function can access a variable declared in its parent environment
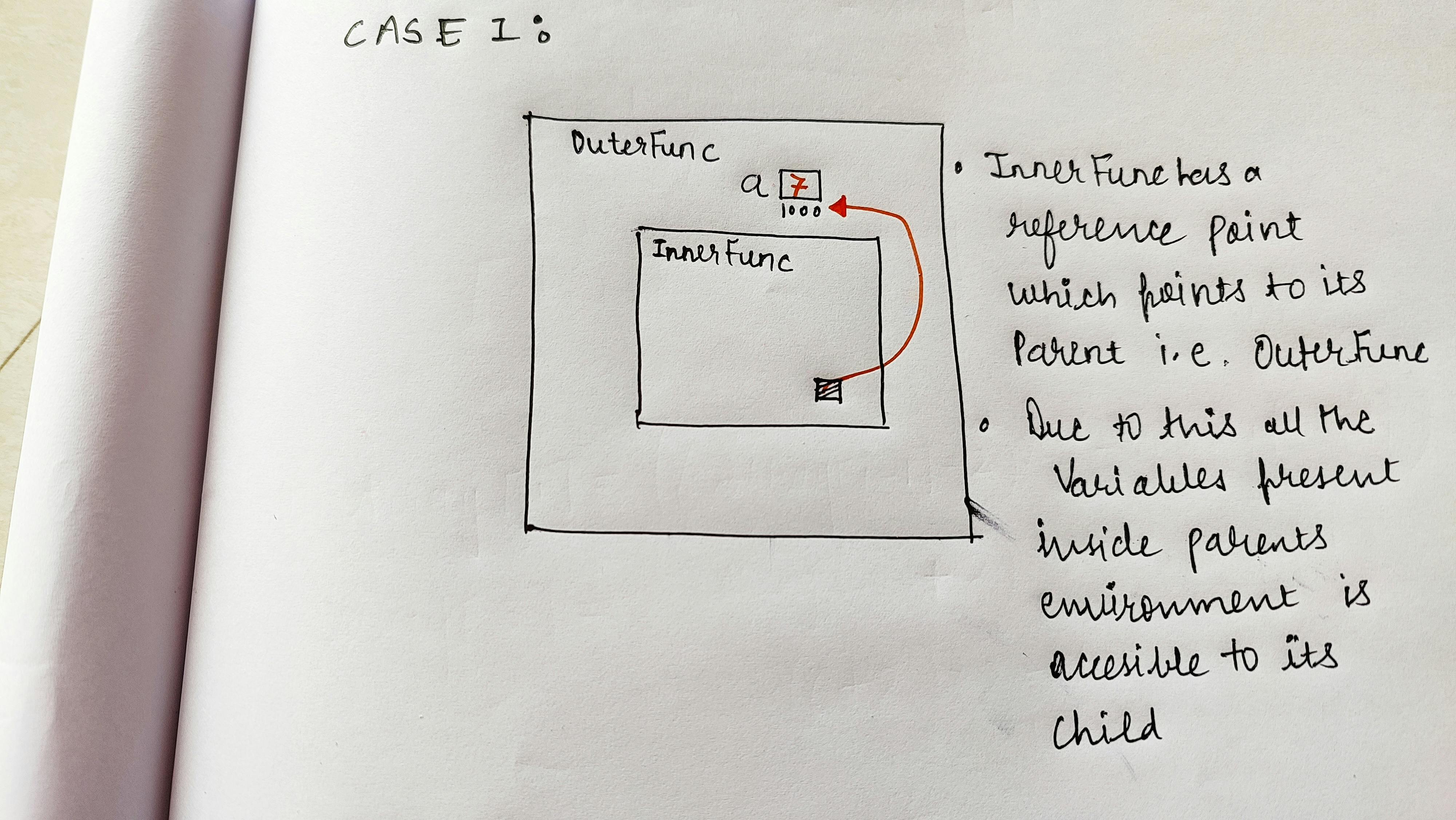
- Closure gives access to scope of outer function from inner function.
To understand this, we first need to understand how execution context is created and how call stack works
- Whenever javascript function runs, execution context is created called
global execution contextand it is put it in call stack. - Whenever a function is invoked or called , it is place into call stack by creating the function's execution context.
- As we know that stack is LIFO (Last In First Out ) data structure, the data which is put on top of stack comes out first
- Whenever a function is put into stack , it has information about where it is currently present in code, that is its lexical environment.
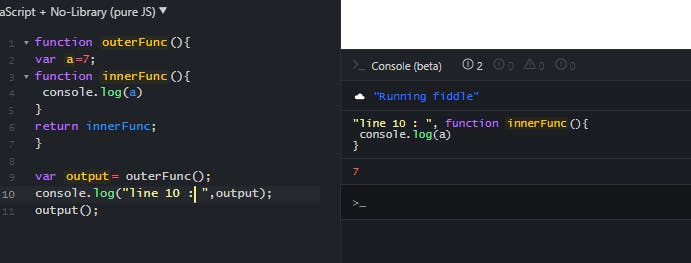
- Consider below code snippet, the function outerFunc() is called on line 9
Example 1 :
- The OuterFunc() has a function called innerFunc() inside it which it returns, In javascript we can use function name as variable name to return like this.
- InnerFunc() doesn't contain any variable declaration or function definition of its own
- If we see output in screenshot,on line 10 whole innerFunc() is returned.
- if we invoke the return value as function , we can see innerFunc() is getting executed, though the outerFunc() ends on line 7, the value of a is accessible in inner environment through lexical scoping and therfore
a'svalue is printed on line4.
- Can you guess the output of the below snippet ?
Example 2:
- The temptation to answer will be
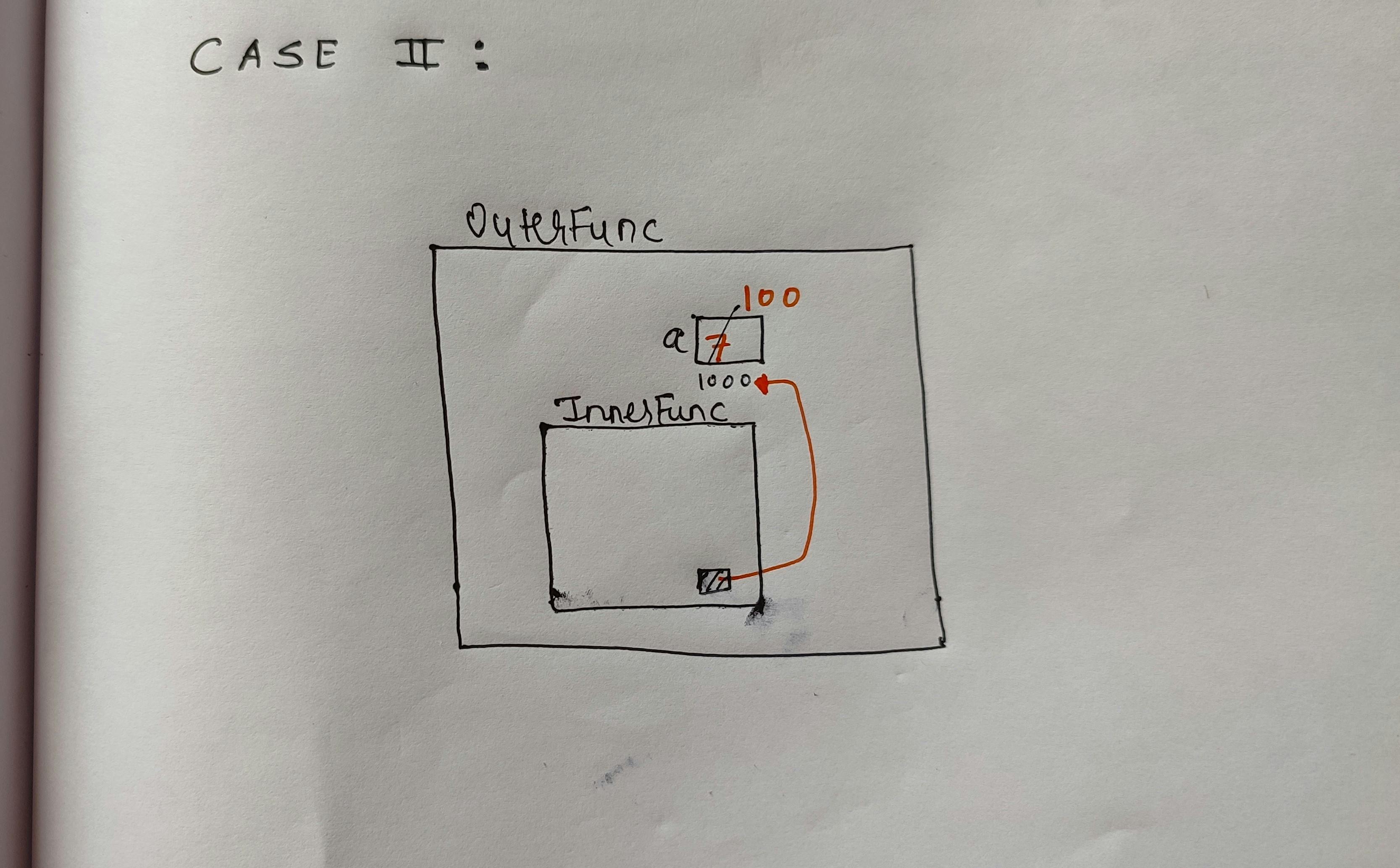
7, but all things change because of line 6 and makes output as8How? lets see - On line 10, outerFunc() is invoked which gets in return the value of innerFunc() same as example 1
- What differs is on line 6, value of
ais reinitialized as 8. Though the innerFunc() can access the value ofaas we have seen in example1. It doesn't store a value ofa, but has reference to address ofa. - As of now the address of
ais the same as the previous but the value is now changed to 100.therfore, output changes.
- Thus , in a way closure provides a superpower for accessing data.